gerhardt's test for ketone bodies in urine Urine test ketone bodies reagent ketones tube rothera strip figure detection tests
Gerhardt’s Test: Principle, Procedure, and Result
The Principle of Gerhardt’s Test
Gerhardt’s test, also known as the phenol-sulfuric acid test, is a chemical test used to detect the presence of carbohydrates in a given sample. It is based on the principle that carbohydrates can be dehydrated and subsequently react with concentrated sulfuric acid to form furfural or hydroxymethylfurfural compounds. These compounds react with phenol to give a colored complex, which can be quantitatively measured.
The Procedure of Gerhardt’s Test
The procedure for Gerhardt’s test is relatively simple and straightforward:
- Prepare a known quantity of the carbohydrate solution to be tested in a test tube.
- Add an equal volume of concentrated sulfuric acid to the test tube. Care should be taken as concentrated sulfuric acid is highly corrosive and should be handled with caution.
- Mix the contents of the test tube gently by swirling it and allow it to stand for 10 minutes at room temperature.
- Add an equal volume of 5% phenol solution to the test tube and mix well again.
- After a few minutes, observe the color development. The presence of carbohydrates will result in the formation of a characteristic color, ranging from yellow to reddish-brown.
The Result of Gerhardt’s Test
The result of Gerhardt’s test is interpreted based on the color produced:
- A yellow color indicates the presence of a small amount of carbohydrates.
- An orange color indicates a moderate amount of carbohydrates.
- A red or reddish-brown color indicates a large amount of carbohydrates.
- No color change indicates the absence of carbohydrates.

Urine Analysis: Urine for Ketones and Ketone Bodies
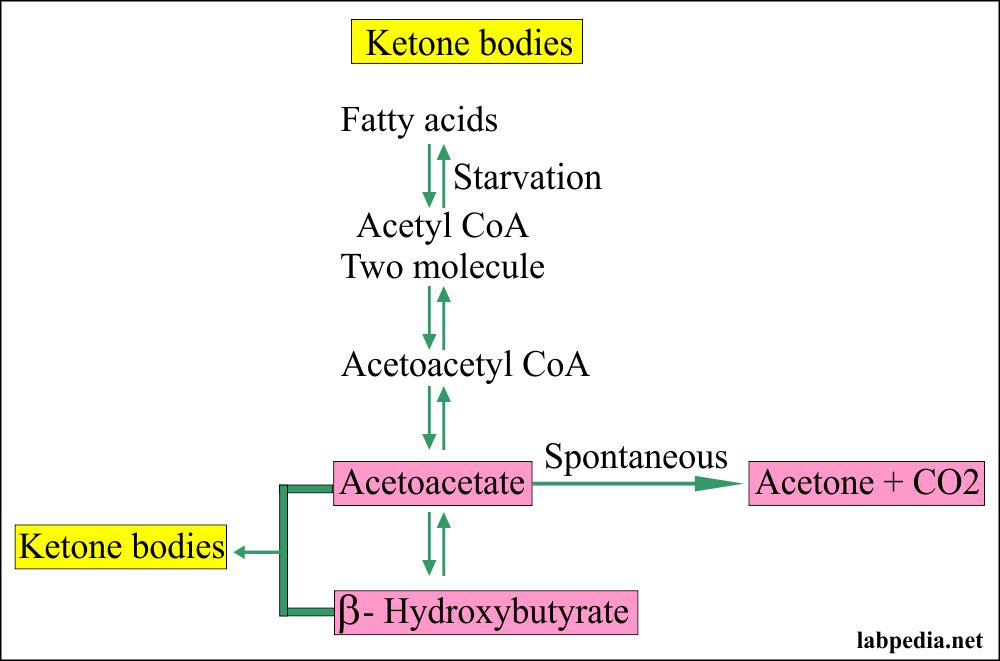
What are Ketones and Ketone Bodies?
Ketones are organic compounds produced by the liver when there is an insufficient supply of glucose for energy production. They are formed from the breakdown of fatty acids and can be used as an alternative energy source. Ketone bodies, including acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone, are the specific ketones produced during this process.
The Significance of Urine Analysis for Ketones
Urine analysis for ketones is performed to detect and monitor ketosis, a metabolic state characterized by elevated levels of ketone bodies in the blood. Ketosis can occur in various conditions such as uncontrolled diabetes, starvation, high-fat diets, and certain metabolic disorders. It is important to monitor ketone levels, as excessive ketone production can be a sign of inadequate insulin levels or other underlying health issues.
The Procedure for Urine Analysis for Ketones
The procedure for urine analysis for ketones involves the following steps:
- Collect a fresh urine sample in a clean, sterile container.
- Dip a ketone test strip into the urine sample or apply a few drops of urine onto the test strip.
- Allow the test strip to react with the urine for a specified period, usually a few seconds.
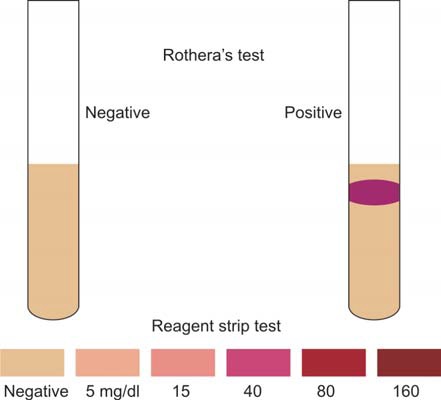
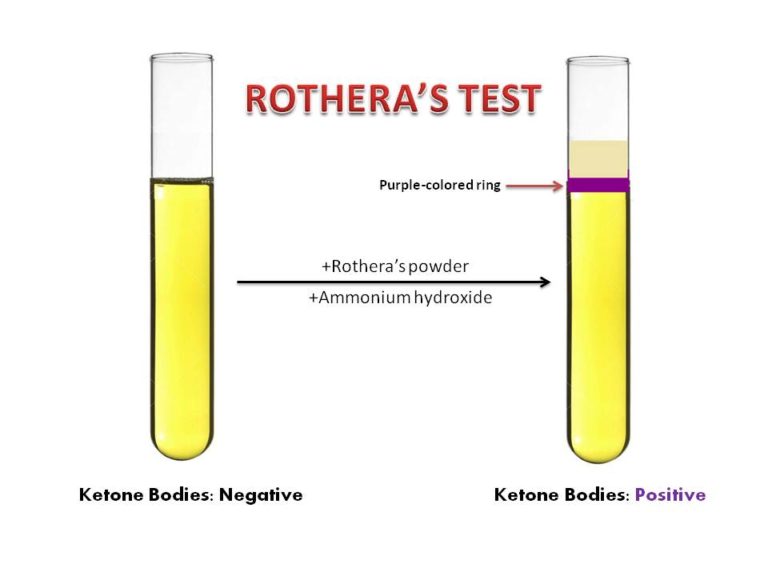
- Compare the color change on the test strip with the provided color chart. Different shades of color indicate varying levels of ketone bodies present in the urine.
- Record the result and interpret it accordingly based on the specific reference range.
In conclusion, Gerhardt’s test is a valuable tool for detecting the presence of carbohydrates, while urine analysis for ketones provides insights into ketone body production. These tests play crucial roles in various fields, such as medical diagnostics, research, and quality control in food industries. It is important to follow the specified procedures and interpret the results accurately to utilize these tests effectively.
If you are searching about TESTS FOR DETECTION OF KETONES IN URINE you’ve came to the right place. We have 5 Pics about TESTS FOR DETECTION OF KETONES IN URINE like Gerhardt’s test Principle, Procedure, Result., Test for Ketone bodies in Urine (Gerhardt’s test) and also Urine Analysis: Part 27 – Urine for ketones, and Ketone Bodies. Read more:
TESTS FOR DETECTION OF KETONES IN URINE
 www.bioscience.com.pkurine test ketone bodies reagent ketones tube rothera strip figure detection tests
www.bioscience.com.pkurine test ketone bodies reagent ketones tube rothera strip figure detection tests
Gerhardt’s Test For Ketone Bodies: Principle, Procedure And Interpretation
 laboratorytests.orgrothera gerhardt ketone biochemistry principle clinical interpretation observations significances
laboratorytests.orgrothera gerhardt ketone biochemistry principle clinical interpretation observations significances
Urine Analysis: Part 27 – Urine For Ketones, And Ketone Bodies
 www.labpedia.netketone bodies ketones formation urine analysis part labpedia metabolism
www.labpedia.netketone bodies ketones formation urine analysis part labpedia metabolism
Test For Ketone Bodies In Urine (Gerhardt’s Test)
 www.awesomebiochem.comGerhardt’s Test Principle, Procedure, Result.
www.awesomebiochem.comGerhardt’s Test Principle, Procedure, Result.
 microbiologynote.comgerhardt gerhardts principle microbiologynote
microbiologynote.comgerhardt gerhardts principle microbiologynote
Urine test ketone bodies reagent ketones tube rothera strip figure detection tests. Gerhardt’s test for ketone bodies: principle, procedure and interpretation. Tests for detection of ketones in urine